The Complete Guide to Varicose Vein Management
Key Takeaways:
- Varicose veins are enlarged, twisted veins that appear on the surface of the skin, usually in the legs.
- Causes and risk factors for varicose veins include age, gender, family history, obesity, and prolonged standing or sitting.
- Symptoms of varicose veins include pain, swelling, heaviness, burning, itching, and visible veins.
- Treatment options for varicose veins include conservative methods, minimally invasive procedures, and surgical interventions.
- Prevention and lifestyle changes for vein health include avoiding prolonged sitting or standing, elevating the legs, exercising regularly, and maintaining a healthy diet.
- Long-term management strategies involve regular check-ups, continued use of compression stockings, regular exercise, healthy weight management, and preventing blood clots.
- Self-care tips for varicose veins include elevating the legs, taking regular exercise breaks, applying cold compresses, avoiding tight clothing, and managing weight.
- Seek medical help if experiencing persistent pain or discomfort, ulcers or sores, bleeding, or symptoms of deep vein thrombosis (DVT).
Understanding Varicose Veins
Varicose veins are a common condition that affects many people around the world. They are enlarged, twisted veins that appear on the surface of the skin, usually in the legs. These veins are caused by weakened valves and walls, which allow blood to flow backwards and pool in the veins. Varicose veins can be unsightly and uncomfortable, causing symptoms such as pain, swelling, and fatigue in the legs.
What are Varicose Veins?
Varicose veins are veins that have become swollen and twisted, usually appearing blue or purple in color. They are most commonly found in the legs and are caused by a condition called venous insufficiency. This occurs when the valves in the veins that help blood flow towards the heart become weak or damaged, causing blood to pool and veins to enlarge.
Varicose veins can be easily visible on the skin’s surface and may appear as bulging or ropelike veins. They can cause a variety of symptoms, including aching, heaviness, and discomfort in the legs. Although they are generally harmless, varicose veins can sometimes lead to more serious complications such as blood clots or ulcers.
Causes and Risk Factors
There are several factors that can contribute to the development of varicose veins. Some common causes include:
- Age: As we age, the risk of developing varicose veins increases. This is because the valves in the veins tend to weaken over time.
- Gender: Women are more likely to develop varicose veins than men. Hormonal changes during pregnancy and menopause, as well as the use of hormonal birth control, can increase the risk.
- Family history: If you have a close family member with varicose veins, you are more likely to develop them as well.
- Obesity: Excess weight puts added pressure on the veins, making them more prone to becoming varicose.
- Prolonged standing or sitting: Jobs that require long periods of standing or sitting can increase the risk of varicose veins.
While these factors can increase the likelihood of developing varicose veins, anyone can be affected. It is important to be aware of the risk factors and take steps to prevent and manage the condition.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
The symptoms of varicose veins can vary from person to person. Some common symptoms include:
- Pain or aching: Many people with varicose veins experience pain or aching in the legs, especially after prolonged periods of standing or sitting.
- Swelling: Varicose veins can cause swelling in the legs and ankles, especially at the end of the day.
- Heaviness or fatigue: The legs may feel heavy or tired, particularly after physical activity.
- Burning or itching: Some people with varicose veins may experience a burning or itching sensation on the skin.
- Visible veins: Varicose veins are often easily visible on the skin’s surface, appearing as bulging or twisted veins.
If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, it is important to see a healthcare provider for a proper diagnosis. They will likely perform a physical examination and may order additional tests, such as an ultrasound, to evaluate the extent of the varicose veins and rule out any underlying conditions.
Treatment Options for Varicose Veins
There are several treatment options available for varicose veins, depending on the severity of the condition and the symptoms experienced. These treatment options can be classified into three main categories: conservative treatment methods, minimally invasive procedures, and surgical interventions.
Conservative Treatment Methods
Conservative treatment methods are often the first line of defense for managing varicose veins. These methods focus on relieving symptoms and improving overall vein health. Some common conservative treatment methods include:
- Compression stockings: Wearing compression stockings can help improve blood flow and reduce swelling in the legs. These stockings apply pressure to the legs, helping to support the veins and prevent blood from pooling.
- Elevation: Elevating the legs above the heart can help reduce swelling and relieve discomfort. This can be done by propping the legs up on a pillow or using a reclining chair.
- Exercise: Regular exercise, especially activities that promote calf muscle movement, can help improve circulation and reduce symptoms of varicose veins.
- Weight management: Maintaining a healthy weight can help reduce the pressure on the veins and prevent further damage.
- Healthy diet: Eating a balanced diet rich in fiber, antioxidants, and vitamins can support overall vein health.
Conservative approaches can be beneficial for varicose vein management and symptom relief. However, they may not completely remove the veins, and some individuals may require additional treatments to fully address the condition.
Minimally Invasive Procedures
If conservative treatments are not sufficient or if the varicose veins are causing significant discomfort or complications, minimally invasive procedures may be recommended. These procedures are typically performed on an outpatient basis and require minimal downtime. Some common minimally invasive procedures for varicose veins include:
- Sclerotherapy: During sclerotherapy, a solution is injected into the affected veins, causing them to collapse and fade away over time. This procedure is often used for smaller, less severe varicose veins.
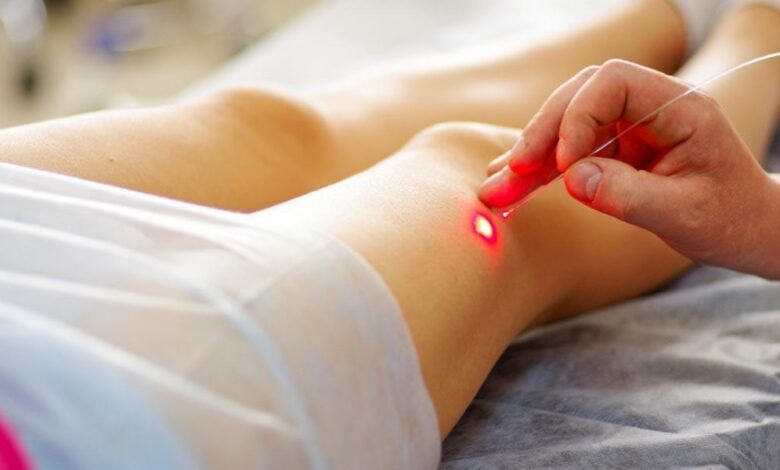
- Endovenous laser therapy (EVLT): EVLT uses laser energy to heat and seal off the affected veins, causing them to close and be reabsorbed by the body. This procedure is often used for larger varicose veins.
- Radiofrequency ablation: Radiofrequency ablation works by delivering heat energy through a catheter to the affected veins, causing them to close and be reabsorbed. This procedure is similar to EVLT and is often used for larger varicose veins.
Minimally invasive procedures offer a less invasive alternative to surgery and can provide effective results for many individuals with varicose veins. They are typically well tolerated and carry fewer risks and complications compared to surgical interventions.
Surgical Interventions
In cases where varicose veins are severe or accompanied by significant complications, surgical interventions may be necessary. Surgical procedures for varicose veins are typically performed under anesthesia in a hospital or surgical center. Some common surgical interventions include:
- Vein ligation and stripping: During vein ligation and stripping, the affected veins are tied off and removed through small incisions in the leg. This procedure is often used for large, bulging varicose veins.
- Ambulatory phlebectomy: Ambulatory phlebectomy involves the removal of smaller varicose veins through tiny incisions in the skin. This procedure is typically performed using local anesthesia.
- Endoscopic vein surgery: Endoscopic vein surgery may be recommended for severe cases of varicose veins. It involves the use of a tiny camera inserted into the leg to visualize and remove the affected veins.
Surgical interventions offer a more invasive treatment option for varicose veins and are typically reserved for cases that cannot be effectively treated with less invasive methods. They may be associated with a longer recovery period and a higher risk of complications compared to minimally invasive procedures.
Prevention and Lifestyle Changes
While varicose veins may not always be preventable, there are steps you can take to reduce your risk and promote overall vein health. Making certain lifestyle changes can help improve circulation and reduce the likelihood of developing varicose veins.
Healthy Habits for Vein Health
Adopting healthy habits can make a significant difference in maintaining vein health and preventing varicose veins. Some healthy habits to consider include:
- Avoiding prolonged periods of sitting or standing: If your job or lifestyle requires long periods of sitting or standing, take regular breaks to move around and improve circulation.
- Elevating the legs: Elevating your legs above the heart for 15 minutes several times a day can help improve circulation and reduce swelling.
- Avoiding tight clothing: Tight clothing, especially around the waist, groin, and legs, can restrict blood flow and increase the risk of varicose veins. Opt for loose-fitting, comfortable clothing instead.
- Avoiding high heels: Wearing high heels for extended periods can contribute to poor circulation and increase the risk of varicose veins. Opt for comfortable shoes with low heels instead.
Exercise and Physical Activity
Regular exercise and physical activity can have numerous benefits for vein health. Engaging in activities that promote muscle movement, especially in the legs, can help improve circulation and strengthen the veins. Some exercises that are beneficial for vein health include:
- Walking: Walking is a low-impact exercise that can be easily incorporated into your daily routine. Aim for at least 30 minutes of brisk walking most days of the week.
- Swimming: Swimming is a great exercise for improving circulation and relieving pressure on the legs. Try swimming laps or taking water aerobics classes.
- Cycling: Cycling is another low-impact exercise that can help improve circulation and strengthen the lower body. Consider cycling outdoors or using a stationary bike.
- Yoga or Pilates: These forms of exercise focus on strength, flexibility, and balance, which can all contribute to improved vein health.
Dietary Recommendations
A healthy diet can support overall vein health and reduce the risk of varicose veins. Some dietary recommendations to consider include:
- Eating a high-fiber diet: A diet rich in fiber can help prevent constipation and improve circulation.
- Consuming foods high in antioxidants: Antioxidant-rich foods, such as berries, citrus fruits, and leafy green vegetables, can help reduce inflammation and support vein health.
- Limiting sodium intake: Consuming excessive amounts of sodium can lead to water retention and swelling. Opt for low-sodium options and avoid adding extra salt to your meals.
- Drinking plenty of water: Staying hydrated can help prevent blood from thickening and improve circulation.
Maintaining Vein Health
While managing varicose veins is important, it is equally crucial to maintain overall vein health and prevent further complications. Long-term management strategies can help minimize symptoms and reduce the risk of complications.
Long-Term Management Strategies
Long-term management of varicose veins involves incorporating healthy habits into your daily routine and following through with ongoing treatments as recommended by your healthcare provider. Some long-term management strategies include:
- Regular check-ups: Schedule regular check-ups with your healthcare provider to monitor the progress of your varicose veins and adjust treatment as needed.
- Continued use of compression stockings: If compression stockings have been recommended, continue to wear them as directed to provide support to the veins and improve circulation.
- Engaging in regular exercise: Maintain a consistent exercise routine to promote circulation and strengthen the veins.
- Healthy weight management: If you are overweight or obese, strive to reach and maintain a healthy weight to reduce the pressure on your veins.
- Preventing blood clots: Follow your healthcare provider’s recommendations for preventing blood clots, such as staying active and avoiding prolonged periods of sitting or standing.
Self-Care Tips for Varicose Veins
In addition to long-term management strategies, there are self-care tips that can help relieve symptoms and improve your overall comfort. Some self-care tips for varicose veins include:
- Elevating the legs: Elevate your legs above the heart whenever possible to reduce swelling and relieve discomfort.
- Regular exercise breaks: If you are sitting or standing for long periods, take regular breaks to walk around and exercise your legs.
- Cold compresses: Applying cold compresses to the affected area can help reduce swelling and relieve pain.
- Avoiding tight clothing: Opt for loose-fitting clothing that does not restrict blood flow.
- Weight management: If you are overweight, losing weight can help reduce the pressure on your veins and alleviate symptoms.
When to Seek Medical Help
While varicose veins are generally harmless, there are times when you should seek medical help. Contact your healthcare provider if you experience any of the following:
- Persistent pain or discomfort: If your varicose veins are causing persistent pain or discomfort that is affecting your quality of life, it is important to seek medical evaluation.
- Ulcers or sores: If you develop ulcers or sores on your legs, it could be a sign of a more serious complication of varicose veins.
- Bleeding: If a varicose vein starts to bleed, apply direct pressure and seek immediate medical attention.
- Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) symptoms: DVT is a serious condition that can occur with varicose veins. Seek medical help if you experience symptoms such as swelling, warmth, and tenderness in the leg.
It is important to remember that varicose veins are a common condition and can usually be managed effectively with the appropriate treatments and lifestyle changes. By taking proactive steps to care for your veins and seeking medical help when needed, you can minimize symptoms and maintain optimal vein health.